Abstract
The use of tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) has dramatically modified the therapy of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML), generating durable remissions and prolonging survival in TKI-responders. However, acquired resistance to TKIs represents a clinical challenge, requiring TKI switch and long-term side effects. TKI-resistance may occur through ABL-kinase domain mutations or by kinase-independent mechanisms such as oncogene independence phenomenon by activation of specific BCR::ABL-independent signaling pathways in leukemic stem cells. The T315I mutation leads to resistance to all TKIs except Ponatinib and Asciminib and confers an aggressive clinical phenotype, especially in advanced stages. Nelfinavir (NFV) is an antiretroviral protease inhibitor drug and used in the treatment of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection. NFV exhibits some anticancer properties in pre-clinical cancer models. Herein, we aimed to investigate the anti-leukemic effect of NFV in CML.
Methods We tested the effects of NFV alone and in combination with Imatinib (IM) or Ponatinib on cell viability by XTT assays in K562 cell line as well as in UT7 cells expressing BCR::ABL (UT7-11) or their T315I-mutated counterparts (UT7-T315I) as compared to parental UT7 cells (UT7p). Cell apoptosis was detected by Annexin V and cells were stained with anti-BrdU-APC and Dapi dyes for cell cycle analysis. γH2Ax expression and Caspase 3 cleavage were demonstrated with Western blots. We have also studied NFV alone or combined with IM in primary CML cells using clonogenic assays from using CD34+ cells from 6 CML patients at diagnosis before any therapy. To understand the molecular mechanisms underlying antitumor activity of NFV, microarray analysis was performed before and after in vitro NFV treatment of UT7p UT7-T315I UT7-11-BCR::ABL for 48 h. To examine metabolic differences between UT7-T315 cells with NFV or DMSO treatments, cellular mitochondrial function was measured by Agilent Seahorse XFp Cell Mito Stress Test.
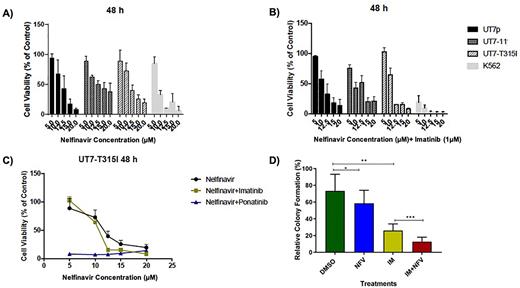
Results NFV significantly decreased the cell viability and induced apoptosis in a dose dependent manner (Figure 1). Furthermore, UT7-T315I cells resistant to IM showed significantly decreased cell viability and increased apoptosis when treated with Ponatinib and NFV as compared to ponatinib alone ( P<0.05). NFV treatment resulted in the arrest of UT7-T315I cells in G1 phase and decreased percentages of cells in the S phase of cell cycle (P<0.001). Additionally, NFV treated cells showed increased γH2Ax expression and Caspase 3 cleavage. NFV treatment reduced oxygen consumption rate in UT7-T315I cells. In clonogenic assays (n= 6 patients) NFV (20 µM) combined with IM (1µM) suppressed CFU-C growth (p <0.0001). Transcriptome data showed an upregulation of 476 genes and down-regulation of 508 genes with fold change over 2 in absolute value and False Discovery Rate less than 5 percent. More specifically, NFV treatment induced the interferon pathways in cells as a part of an inherent immune response to viral infections. Gene-set enrichment analysis (GSEA) showed differential expression in mitotic spindle, apoptosis, eEF2 targets and inflammatory response. eEF2K is the target protein of the NFV that is activated under cellular stress conditions and down regulates translation. We showed that NFV treatment in cell lines triggered eEF2-T56 phosphorylation through eEF2K expression.
Conclusions: We show for the first time that the anti-HIV drug NFV in combination with TKIs could exhibit a highly significant effect in BCR::ABL expressing hematopoietic cells as well as in primary CML samples. Most importantly, low levels of NFV increased the Ponatinib efficiency in T315I-mutated BCR::ABL-expressing cells. These inhibitory effects implicate the activation of eEF2K with induction of interferon pathways. These results suggest that TKIs and NFV in combination may synergize in CML and more specifically, could represent a novel therapeutic approach in patients with the T315I mutation.
Figure 1. Cell viability assay was performed in cell lines treated with indicated concentrations of NFV for 48 hours (A) and in combination with IM (B) or ponatinib (C). IM in combination with NFV significantly reduced the colony numbers of CML patients (n=6) in clonogenic assays. (*p<0.05, ** p<0.005, *** p<0.0005).
Y.E. is supported by the Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey (TÜBİTAK) and Vaincre le Cancer.
Disclosures
Turhan:Abbvie: Consultancy, Honoraria; Incyte Biosciences: Consultancy, Honoraria; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria.
OffLabel Disclosure:
Nelfinavir, an anti HIV drug exhibits cytotoxic activity against BCR-ABL-expressing leukemic cells
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal